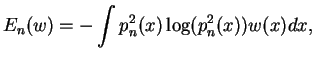[ SCOPE
| PROGRAM
| ABSTRACTS
| WHERE
| PARTICIPANTS
| SUPPORT
| ACCOMODATION
| ORGANIZERS
]
ABSTRACTS
¸ Tanguy Rivoal (Université de Caen):
Title: On the denominator conjecture
Abstract:
Dans cet exposé j'exposerai deux méthodes permettant de
construire de très bonnes approximations rationnelles de la
constante de Catalan
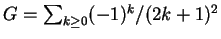 : l'une des
méthodes utilise une série hypergéométrique très bien
équilibrée, la seconde des approximants de Padé.
: l'une des
méthodes utilise une série hypergéométrique très bien
équilibrée, la seconde des approximants de Padé.
Numériquement, la première construction n'est pas optimale en
un sens précis ("Conjecture des dénominateurs") :
j'indiquerai comment, de façon surprenante, la deuxième
construction permet de prouver cette conjecture.
Malheureusement, ces approximations rationnelles ne suffisent pas
à montrer l'irrationalité de G, qui reste un problème
ouvert.
¸ Walter Van Assche (University of Leuven):
Title: Differential and difference equations for multiple orthogonal polynomials
Abstract:
The classical orthogonal polynomials (Jacobi, Laguerre, Hermite)
all satisfy a linear second order differential equation of
Sturm-Liouville type. Other polynomials from the Askey table
satisfy a second order difference or q-difference equation.
We will show that several multiple orthogonal polynomials
also satisfy a differential or difference equation, but of
higher order.
¸ Pascale Vitse (Université de Besançon):
Title: Free interpolation by polynomials of a given degree
Abstract:
We give a polynomial version of the Carleson free interpolation theorem
for
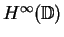 , that is free interpolation by polynomials
with controlled degree and norm (the uniform norm on the unit disc).
More precisely, given a Carleson sequence
, that is free interpolation by polynomials
with controlled degree and norm (the uniform norm on the unit disc).
More precisely, given a Carleson sequence
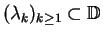 ,
and given an integer
,
and given an integer 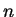 , what is the largest disc
, what is the largest disc 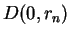 such that
one can interpolate at all points
such that
one can interpolate at all points 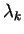 in this disc by a polynomial
of degree at most
in this disc by a polynomial
of degree at most 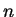 with a control of the norm independant of
with a control of the norm independant of 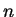 .
An answer is given by the following theorem:
.
An answer is given by the following theorem:
Theorem Let
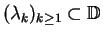 be a Carleson
sequence
with constant
be a Carleson
sequence
with constant 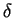 ,
, 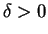 , and let
, and let 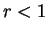 .
For every
.
For every
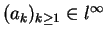 , there exists a polynomial
, there exists a polynomial 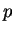 of degree at most
of degree at most
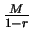 such that
such that
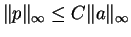 and
and
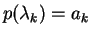 si
si
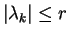 , where
, where 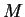 and
and 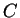 are some
constants depending only on
are some
constants depending only on 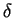 .
.
The proof consists in an iterated approximation of a solution.
¸ Alexandre Aptekarev (University of Moscow):
Title: Trajectories of quadratic differentials on algebraic Riemann surfaces and Hermite-Padé approxiamnts
Abstract:
Rational Hermite-Pade approximants for a set of functions with separated
branch points is considered. The poles of approximants and extra
interpolation points are
distributed along the extremal curves, which are the trajectories of
quadratic differentials on algebraic Riemann surface. The Riemann
surface depends on the
disposition of the branch points of approximated functions. The most
interesting phenomenon is the change of the genus of the Riemann surface
when the branch
points of the functions pass through certain critical dispositions. We
make an attempt to describe these bifurcations in the special case of
the two functions, each of
them has two branch points.
¸ Reinhold Küstner (UST Lille):
Title: On the zero distribution of certain non Hermitian orthogonal polynomials
Abstract:
We are dealing with the zero distribution of non-Hermitian orthogonal
polynomials
which arise as the denominators of Padé / rational / meromorphic
approximants of the
Cauchy transform of a complex Borel measure having compact support K
contained in
the real line / in (-1,1).
Under the assumption that the argument of the measure is the restriction
of a function
of bounded variation it is possibe to obtain geometric constraints for
the zeros of the orthogonal polynomials which imply that all weak* limit
measures of the corresponding zero counting (probability) measures have
support included in K. With an additional hypothesis on the density of
the measure it then follows that the zero counting measures converge
weakly* to the logarithmic / hyperbolic equilibrium distribution of K.
¸ Laurent Baratchart (INRIA Nice):
Title: Singular vectors of Hankel operators and normality
Abstract:
On considère le problème de savoir quand les vecteurs singuliers
normalisés de
l'opérateur de Hankel
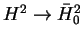 de symbole
de symbole
où 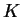 est un compact du disque unité ouvert,
ont des facteur extérieurs qui forment une famille normale dans le
complémentaire de K. Ceci est une question-clef pour déterminer le
comportement asymptotique des pôles des meilleurs approximants
méromorphes de f sur le cercle via la téorie AAK, et c'est aussi un
témoin important de la nature des multiplicités. Par exemple, si la
normalité de la famille ci-dessu a lieu, seul un nombre fini de pôles
peut rester dans un compact disjoint de K, et les multiplicités sont
bornées.
est un compact du disque unité ouvert,
ont des facteur extérieurs qui forment une famille normale dans le
complémentaire de K. Ceci est une question-clef pour déterminer le
comportement asymptotique des pôles des meilleurs approximants
méromorphes de f sur le cercle via la téorie AAK, et c'est aussi un
témoin important de la nature des multiplicités. Par exemple, si la
normalité de la famille ci-dessu a lieu, seul un nombre fini de pôles
peut rester dans un compact disjoint de K, et les multiplicités sont
bornées.
Dans le cas où K est une géodésique hyperbolique,
le résultat sous hypothèse que l'argument de n est à variation
bornée est obtenu dans les thèses de F. Mandrea et R. Küstner.
On examinera le cas d'un contour symétrique général pour le potentiel de
Green, et on émettra quelques hypothèses sur le cas de compact K plus
généraux.
¸ Stefan Becuwe (University of Antwerpen):
Title: Fast and validated computation of multivariate rational approxiamnts with applications
Abstract:
In this talk we discuss two applications that each need another type
of rational approximant and in the same time we sketch some of the
research carried out in Antwerp.
In the first application we try to model microwave circuits. A
bivariate model is constructed. The model is being updated in a
specific way till a given criterion is met. This new way of updating
achieves much better results than those known before. The underlying
technique is multivariate rational interpolation.
The second application is shape reconstruction. The relationship
between the Radon transform, the Markov transform and the
2-dimensional Stieltjes transform, together with the Pade slice
theorem, lets us reconstruct objects without using interpolation
techniques, as was done in the past. To actually compute the
reconstruction, we need multivariate homogeneous Pade approximants.
We describe a method, based on GKO, to compute both multivariate
approximants with the same tools. A verification step is added to
obtain a validated result.
¸ Herbert Stahl (TFH Berlin):
Title: Asymptotics of Hermite-Padé
Polynomials associated with the exponential function
Abstract:
Hermite-Padé polynomials and approximants are in a very natural
way generalizations of Padé approximants and continued
fractions. Historically, they are, perhaps, most famous for their
role in Hermite's proof of the transcendency of the number e,
and for a long time they have only been a topic for specialists in
analytic number theory.
Within the last 15 years, however, there
has been a considerable up-swing of interest in this topic in
complex and constructive approximation theory, where the field is
typically connected with questions like multiple orthogonality,
higher order recurrence relations, or the approximation of
functions with branch points. But despite of much progress,
many of the basic questions
about convergence and asymptotics are still open.
The talk will be based on
recent research about quadratic Hermite-Padé polynomials
associated with the exponential function. After a somewhat broader
introduction, new results are presented, and some
time will be spent with the main tools that have made progress possible.
A prominent place is taken here by a concrete compact Riemann surfaces
of an algebraic function of third degree.
Looking ahead to investigations
of problems beyond the quadratic case will demand the
analysis of more complex compact Riemann surfaces.
¸ Franck Wielonsky (UST Lille):
Title: Entropy of orthogonal polynomials in the Szegö class
Abstract:
We describe an asymptotic upper bound as
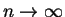 for the entropy
integral, that appears e.g. in the study of the wave function of some
important systems in quantum mechanics,
for the entropy
integral, that appears e.g. in the study of the wave function of some
important systems in quantum mechanics,
where 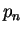 is the
is the 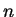 th degree orthonormal polynomial with respect to a
weight
th degree orthonormal polynomial with respect to a
weight 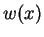 on
on ![$ [-1,1]$](ja2_abstracts/img31.gif) which belongs to the Szego class. The entropy
integral may be decomposed in a natural way as a sum of two functionals which
are also studied, as well as some universal behavior (i.e. independent of the
weight) of related
quantities. When the weight belongs to the Bernstein class, the asymptotic
properties can be completely described.
which belongs to the Szego class. The entropy
integral may be decomposed in a natural way as a sum of two functionals which
are also studied, as well as some universal behavior (i.e. independent of the
weight) of related
quantities. When the weight belongs to the Bernstein class, the asymptotic
properties can be completely described.
This is a joint work with B. Beckermann, A. Martinez-Finkelshtein, and
E.A. Rakhmanov.
ACM (matos@math.univ-lille1.fr), March 4, 2004